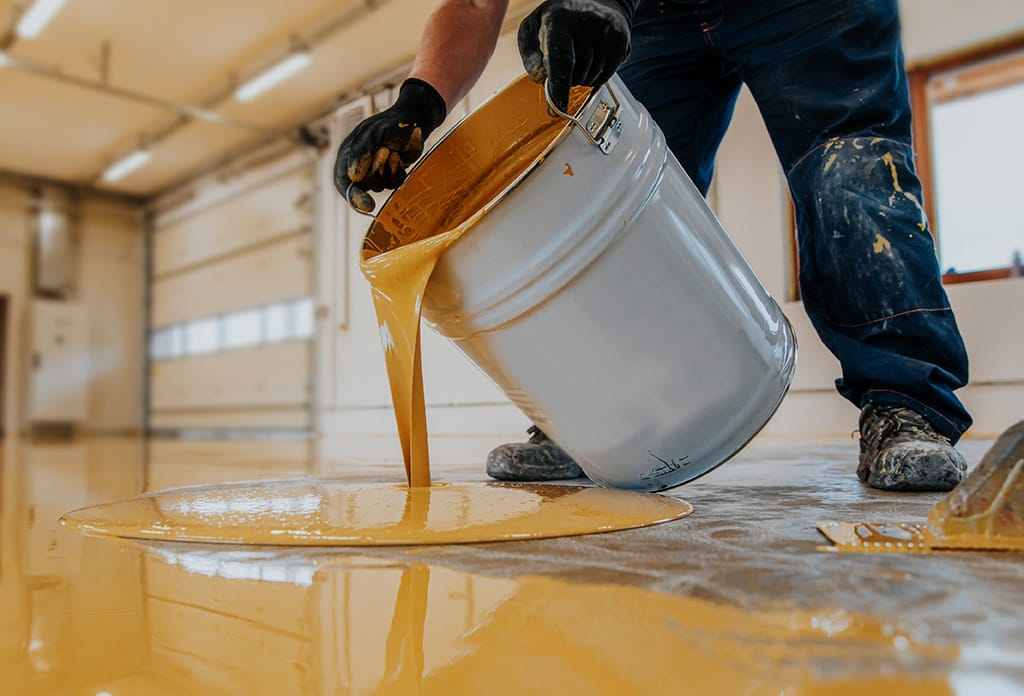
What are Epoxy Resins?
Epoxy resins are a class of thermosetting polymers that cure when mixed with a hardening agent, creating a durable, adhesive, and chemical-resistant material. Known for their exceptional bonding strength and versatility, epoxy resins are widely used across various industries, including construction.
In frame house construction, epoxy resins are primarily used as adhesives, sealants, coatings, and composite materials. Their ability to strengthen structural components, protect surfaces, and provide water resistance makes them an essential material in modern building techniques.
History and Origin of Epoxy Resins
Epoxy resins were first developed in the 1930s by Dr. Pierre Castan in Switzerland and Dr. Sylvan Greenlee in the United States. Initially used in industrial applications, their versatility and strength quickly led to widespread adoption in construction, aerospace, and automotive industries.

The technology behind epoxy resins has since evolved to include formulations designed for specific uses, such as high-strength adhesives, waterproof coatings, and structural composites. Today, epoxy resins are a cornerstone material in both traditional and innovative construction practices.
Applications in Frame House Construction
Epoxy resins are utilized in various ways in frame house construction, offering structural reinforcement and surface protection. Key applications include:
• Adhesives: Used to bond wood, metal, and composite materials, epoxy ensures strong and durable connections in structural and decorative elements.
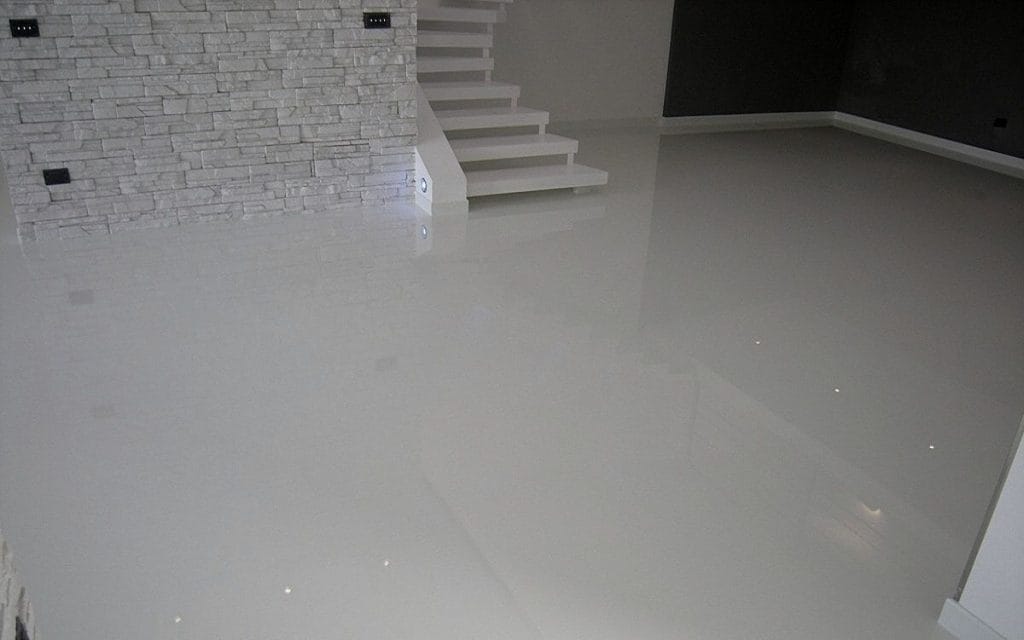
• Surface Coatings: Applied as protective layers for floors, walls, and wooden beams, epoxy coatings provide water resistance, abrasion resistance, and a polished finish.
• Structural Reinforcement: Combined with fiberglass or carbon fiber, epoxy resins create high-strength composites for beams, panels, and load-bearing components.
• Crack Repairs: Used to fill and seal cracks in concrete foundations, walls, and other structural components, preventing water infiltration and further damage.
• Moisture Barrier: Epoxy is applied to protect wooden frames and other vulnerable materials from moisture, increasing the lifespan of the structure.
Leading Manufacturers of Epoxy Resins
Several global manufacturers produce high-quality epoxy resins tailored for construction purposes. Leading companies include:
1. Hexion Inc. (USA): One of the largest producers of epoxy resins, offering products designed for structural adhesives and coatings.
2. Olin Corporation (USA): Known for its D.E.R.™ epoxy resins, widely used in construction and industrial applications.
3. Huntsman Corporation (USA): Specializes in advanced epoxy formulations for adhesives, composites, and coatings.
4. Sika Group (Switzerland): Offers epoxy products for construction, including crack fillers, sealants, and protective coatings.
5. BASF SE (Germany): Produces epoxy systems for structural bonding, waterproofing, and high-performance composites.
These manufacturers focus on innovation, durability, and sustainability to meet the demands of modern construction.
Costs and Economic Feasibility
The cost of epoxy resins depends on the formulation, application, and brand. In the U.S., average prices are:

• General-Purpose Epoxy Resin: $60–$100 per gallon.
• High-Performance Structural Adhesives: $5.00–$10.00 per square foot, depending on the thickness and application.
• Epoxy Floor Coatings: $3.00–$12.00 per square foot, including materials and labor.
While epoxy resins are not the cheapest materials, their durability, strength, and multi-functional properties provide excellent long-term value, reducing maintenance and repair costs over time.
Advantages of Epoxy Resins
1. Exceptional Bonding Strength: Epoxy creates a strong, durable bond between materials, ensuring structural integrity in critical connections.
2. Waterproofing and Moisture Resistance: Epoxy coatings protect surfaces from water damage, making them ideal for areas prone to moisture exposure.
3. Durability and Longevity: Epoxy resins resist wear, chemicals, and environmental factors, extending the lifespan of treated materials.
4. Versatility: Suitable for adhesives, coatings, and composites, epoxy resins can be used in a wide range of applications.
5. Aesthetic Finish: Epoxy coatings provide a glossy, polished surface that enhances the appearance of floors, walls, and decorative elements.
6. Chemical Resistance: Epoxy resists oils, acids, and other chemicals, making it suitable for garages, basements, and utility spaces.
7. Fast Curing: Modern epoxy formulations cure quickly, reducing downtime during construction.
Disadvantages of Epoxy Resins
1. Cost: High-quality epoxy resins are relatively expensive compared to traditional adhesives or coatings.
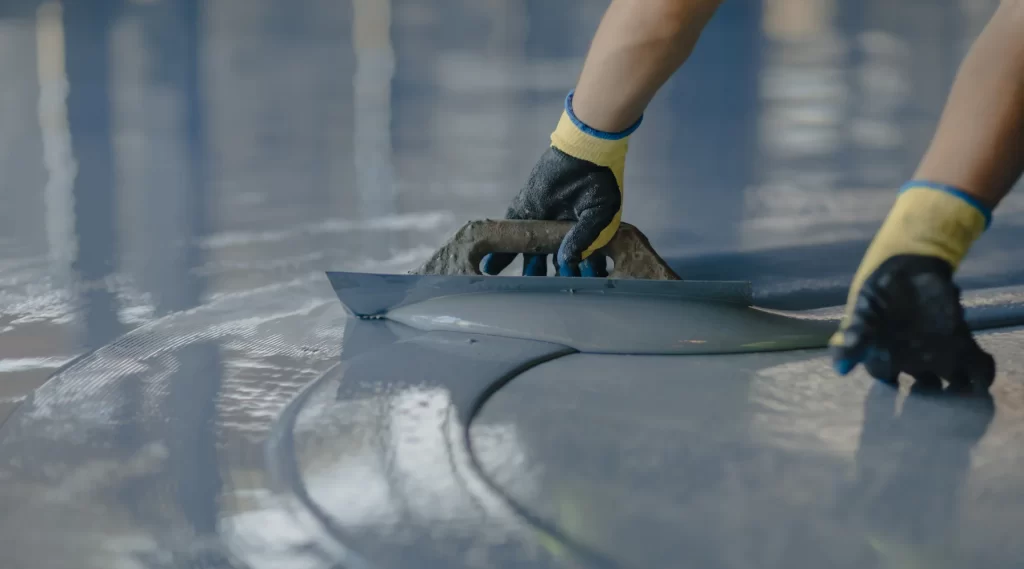

2. Application Sensitivity: Proper mixing and application are crucial; errors can lead to poor performance or curing issues.
3. UV Sensitivity: Unprotected epoxy may yellow or degrade over time when exposed to direct sunlight, requiring UV-resistant coatings for outdoor use.
4. Health and Safety Concerns: Epoxy resins can release fumes and require proper ventilation and protective equipment during application.
5. Brittleness Over Time: Some epoxy formulations may become brittle with age, particularly in high-stress or vibration-prone areas.
6. Limited Flexibility: While strong, epoxy resins lack flexibility, which can be a disadvantage in structures that experience movement or shifting.
Conclusion
Epoxy resins are a versatile and essential material in frame house construction, offering unmatched bonding strength, durability, and resistance to environmental factors. From adhesives to waterproof coatings and high-strength composites, epoxy resins enhance the performance and lifespan of structural and decorative components.
Though they come with some drawbacks, such as cost and application sensitivity, their long-term benefits make them a worthwhile investment. As construction technology advances, epoxy resins will continue to play a vital role in creating stronger, more efficient, and more sustainable buildings.



