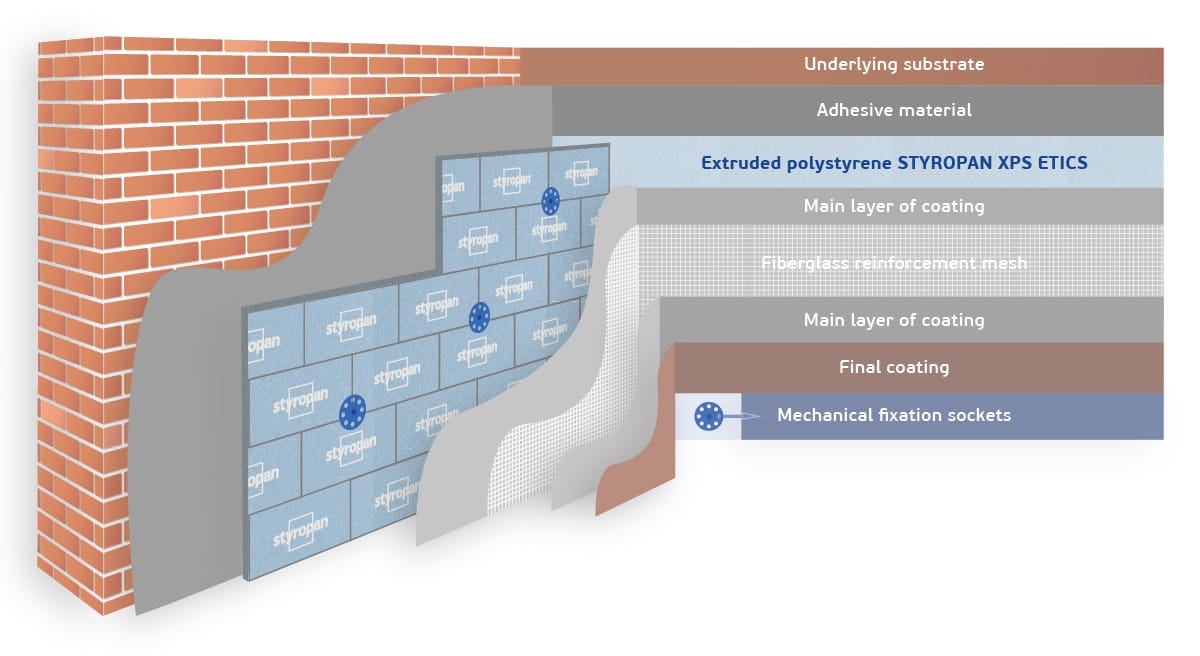
What is Extruded Polystyrene (XPS)?
Extruded polystyrene (XPS) is a rigid foam insulation material made by melting and extruding polystyrene resin. The result is a closed-cell structure that provides excellent thermal insulation, moisture resistance, and compressive strength.
XPS is widely used in frame house construction as an effective insulation material for foundations, walls, roofs, and floors. Its lightweight and durable properties make it an ideal choice for energy-efficient homes.
History and Origin of XPS
XPS insulation was first developed in the 1940s, with Dow Chemical pioneering the manufacturing process. The product, known under the trade name Styrofoam™, quickly gained popularity for its insulation capabilities and versatility.
Since then, XPS has become a global standard for thermal insulation in residential, commercial, and industrial applications. Advances in manufacturing processes and environmental standards have improved the performance and sustainability of XPS over time.
Applications in Frame House Construction
XPS is an essential insulation material in frame house construction, used in the following applications:
• Foundation Insulation: XPS is commonly used to insulate basements, crawlspaces, and slab foundations, as it resists moisture and retains its insulating properties even in damp conditions.
• Wall Insulation: XPS panels can be installed on exterior walls as continuous insulation to reduce thermal bridging and improve energy efficiency.
• Roof Insulation: In flat or sloped roofs, XPS is used as a lightweight, durable insulation layer beneath waterproofing membranes or shingles.
• Floor Insulation: XPS provides thermal insulation for floors, especially in cold climates, and is often used under radiant heating systems.
• Structural Insulated Panels (SIPs): XPS is a core material in SIPs, which are prefabricated panels used to construct walls, roofs, and floors in frame houses.
Leading Manufacturers of XPS Insulation
Several leading manufacturers produce high-quality XPS insulation products for construction. These include:
1. Dow Building Solutions (USA): Known for its Styrofoam™ brand, offering a wide range of XPS insulation panels for residential and commercial use.
2. Owens Corning (USA): Produces FOAMULAR® XPS insulation with high thermal resistance and moisture durability.
3. Kingspan (Ireland): A global leader in insulation products, including XPS panels for walls, roofs, and floors.
4. BASF (Germany): Known for its Styrodur® XPS panels, designed for energy-efficient building envelopes.
5. Austrotherm (Austria): Offers high-performance XPS insulation for construction and industrial applications.
These manufacturers meet strict quality standards and often offer products with environmental certifications, such as low global warming potential (GWP) ratings.
Costs and Economic Feasibility
XPS insulation is a mid-range option in terms of cost, balancing affordability and performance. In the U.S., average prices are:
• Standard XPS Panels (1-inch thickness): $15–$25 per 4×8-foot sheet.

• Thicker XPS Panels (2–4 inches): $25–$50 per 4×8-foot sheet, depending on the thickness and brand.
• Specialty XPS (e.g., high compressive strength): $50–$80 per 4×8-foot sheet.
Labor costs for installing XPS insulation typically range from $0.50 to $1.50 per square foot, depending on the application and complexity. Despite the initial investment, the long-term energy savings and durability of XPS make it a cost-effective choice for frame houses.
Advantages of XPS Insulation
1. Excellent Thermal Performance: XPS has a high R-value (around 5.0 per inch), providing superior insulation and energy efficiency.
2. Moisture Resistance: Its closed-cell structure prevents water absorption, making it ideal for damp environments like basements and foundations.
3. High Compressive Strength: XPS can withstand heavy loads, making it suitable for floors, roofs, and structural applications.
4. Durability: XPS is resistant to rot, mold, and pests, ensuring long-lasting performance.
5. Lightweight and Easy to Install: XPS panels are lightweight, easy to cut, and simple to install, reducing labor time and costs.
6. Versatility: XPS can be used in a wide range of applications, from walls to foundations, roofs, and floors.
7. Energy Efficiency: By reducing heat loss, XPS contributes to lower heating and cooling costs, improving the energy efficiency of homes.
Disadvantages of XPS Insulation
1. Environmental Impact: XPS production involves the use of hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) or other blowing agents with high global warming potential (GWP). However, newer formulations aim to reduce this impact.
2. Flammability: XPS is combustible and must be protected with a fire-resistant covering, such as drywall, in interior applications.
3. Cost: While affordable, XPS is more expensive than some other insulation materials like fiberglass or expanded polystyrene (EPS).
4. Limited Breathability: XPS creates a vapor barrier, which may cause moisture issues in poorly ventilated spaces.
5. UV Sensitivity: Prolonged exposure to sunlight can degrade XPS, requiring protection during installation and in exterior applications.
6. Disposal Concerns: XPS is not biodegradable and can contribute to construction waste if not recycled.
Conclusion
Extruded polystyrene (XPS) is a high-performance insulation material that plays a vital role in frame house construction. Its superior thermal insulation, moisture resistance, and durability make it a reliable choice for foundations, walls, roofs, and floors.
While XPS has some environmental and cost considerations, advancements in manufacturing technology are improving its sustainability and reducing its ecological footprint. For builders and homeowners seeking a durable and efficient insulation solution, XPS remains a practical and effective option for achieving energy-efficient and long-lasting frame houses.