The 5 Most Efficient Options for the U.S. Market
Timber-frame homes are common across the U.S., and the efficiency of heating systems depends on the home’s insulation, regional climate, and energy costs. Below are five popular heating systems, their advantages, and disadvantages, adapted for U.S. homeowners.
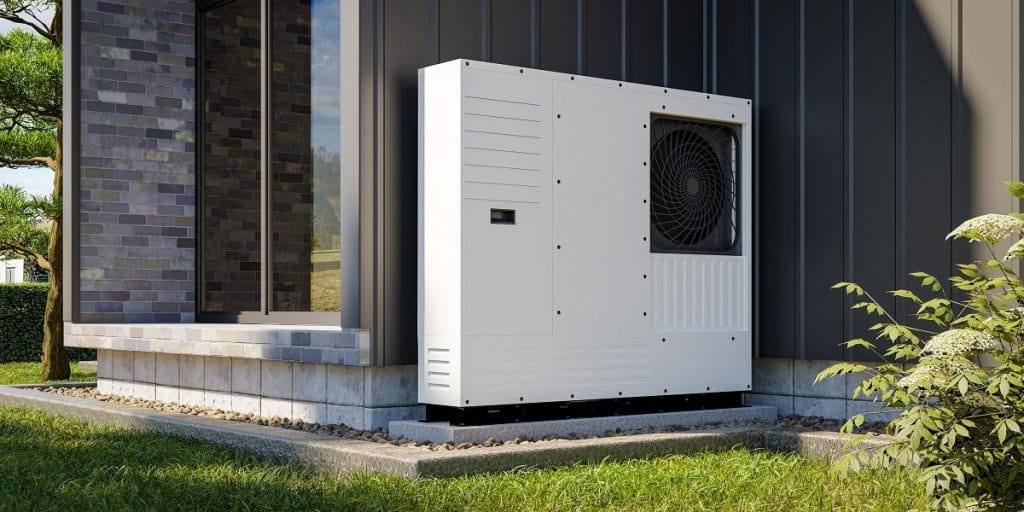
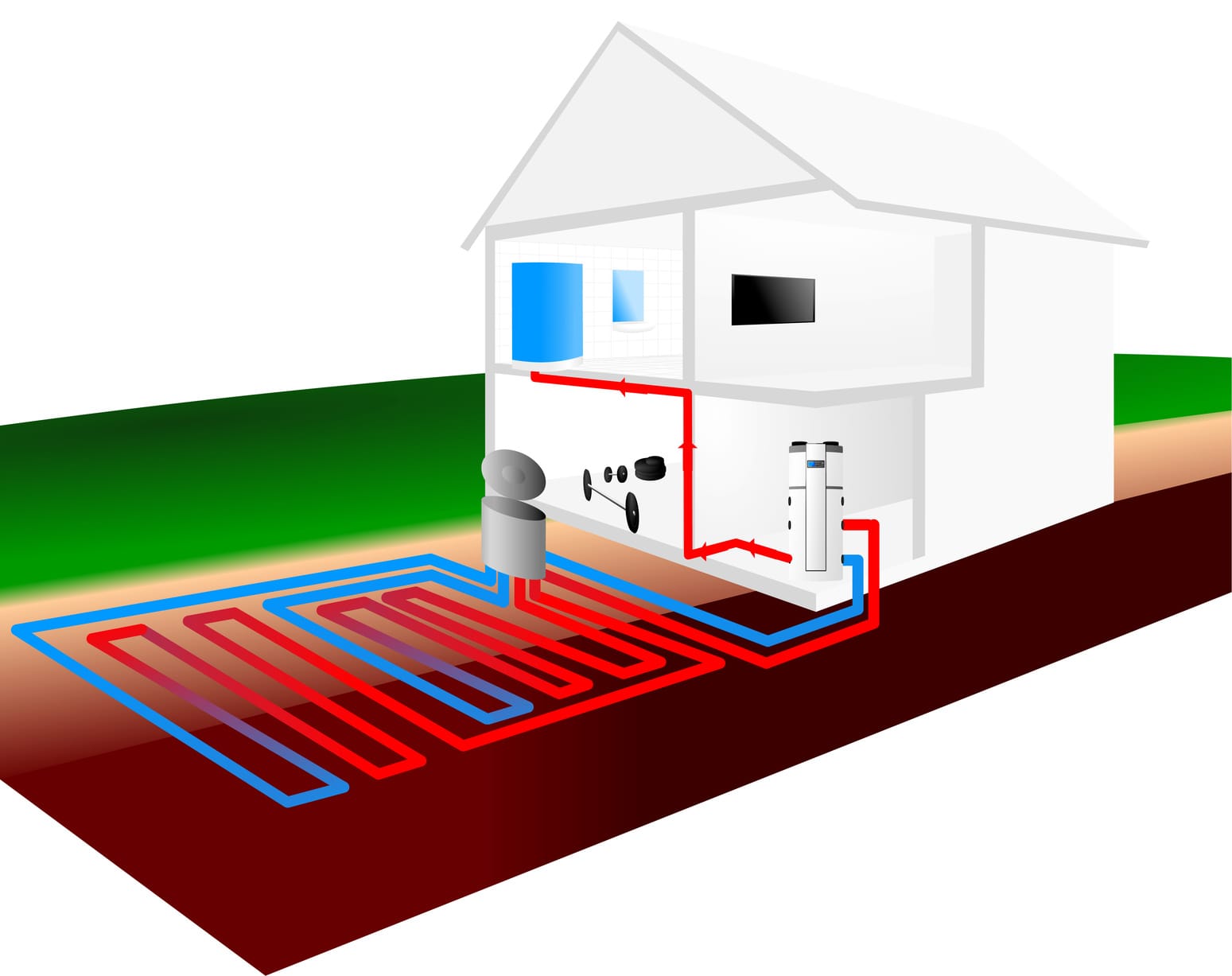
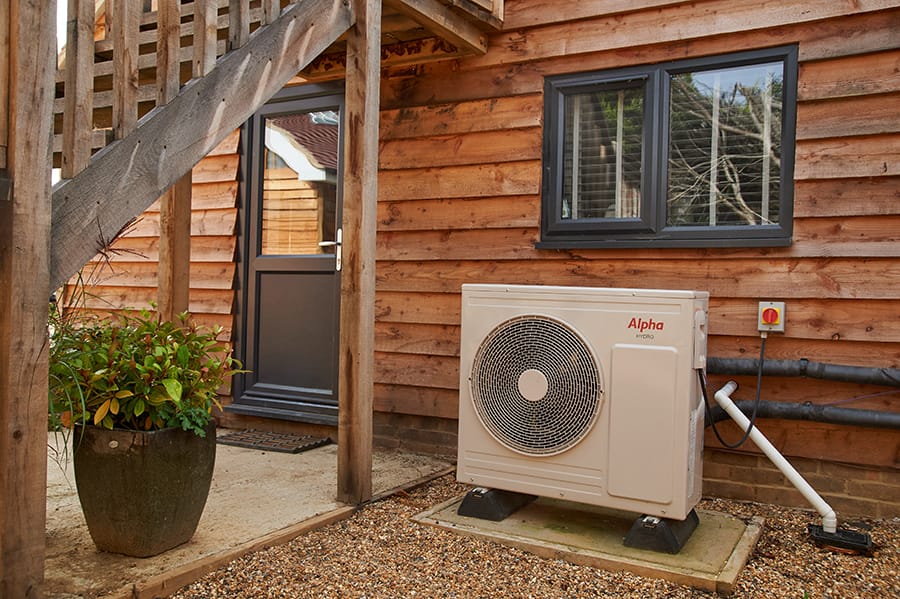
1. Heat Pumps (Air Source or Geothermal)
Advantages:
• Highly energy-efficient (COP > 3, especially for geothermal systems).
• Dual-purpose: provides heating in winter and cooling in summer.
• Environmentally friendly, as they use natural heat sources.
• Air-source heat pumps work well in mild climates, while geothermal systems are effective in any climate.

Disadvantages:
• High upfront costs, particularly for geothermal systems.
• Air-source models lose efficiency in extremely cold weather.
• Require periodic maintenance.
2. Gas Furnaces
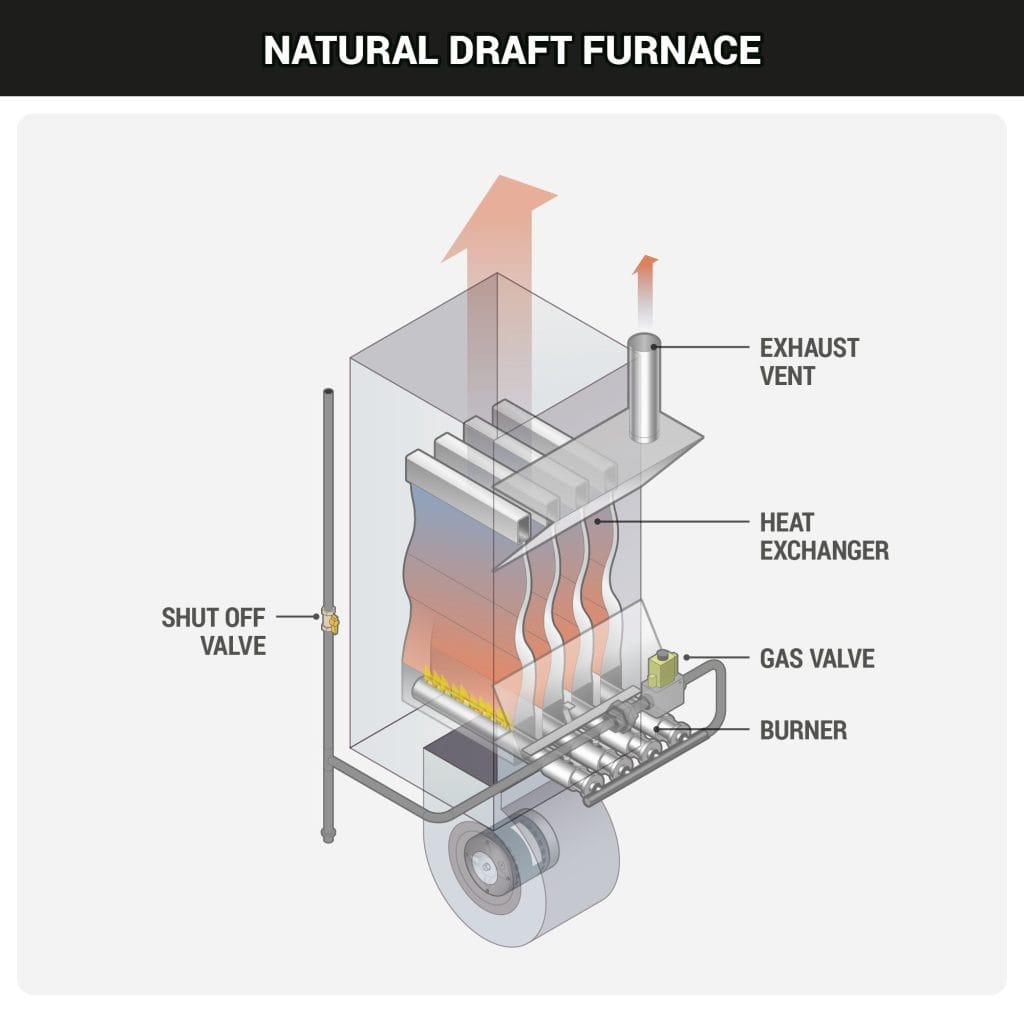
Advantages:
• Widely available and commonly used, especially in colder northern regions.
• Quickly heats the home.
• Cost-effective when natural gas prices are low.
• Extensive infrastructure for gas delivery in most areas.
Disadvantages:
• Dependence on fluctuating gas prices.
• Requires ductwork installation.
• Can be noisy compared to other systems.
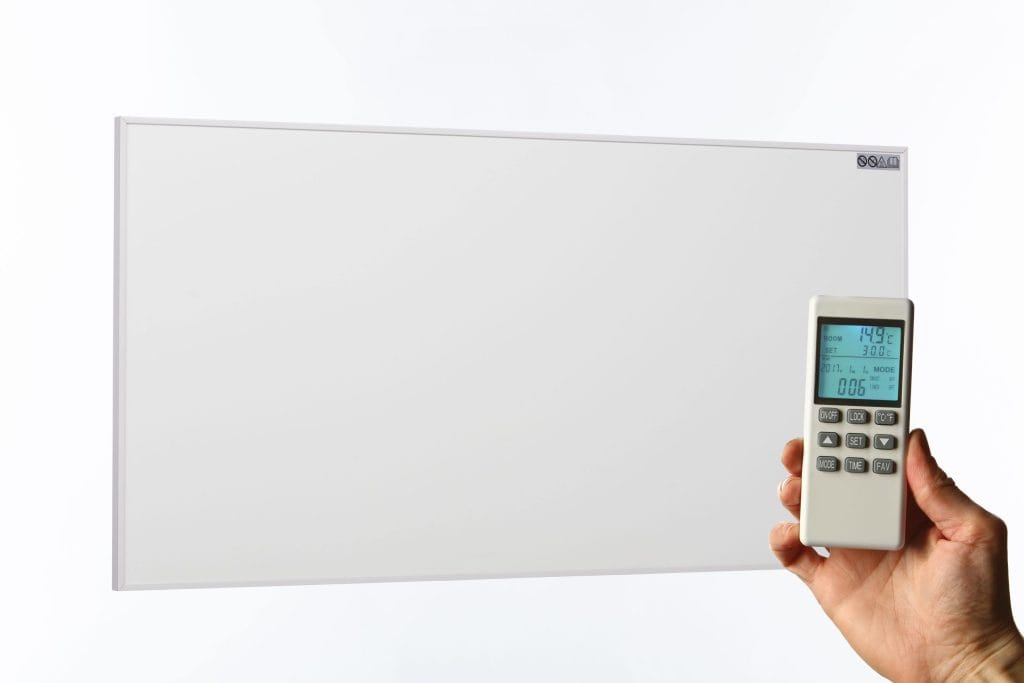
3. Electric Infrared Heaters or Panels

Advantages:
• Simple and affordable installation.
• Ideal for heating specific rooms or spaces.
• No need for ductwork or piping.
• Operates silently.
Disadvantages:
• High operational costs due to electricity prices.
• Not efficient for heating large spaces.
• Limited to heating only; no cooling function.
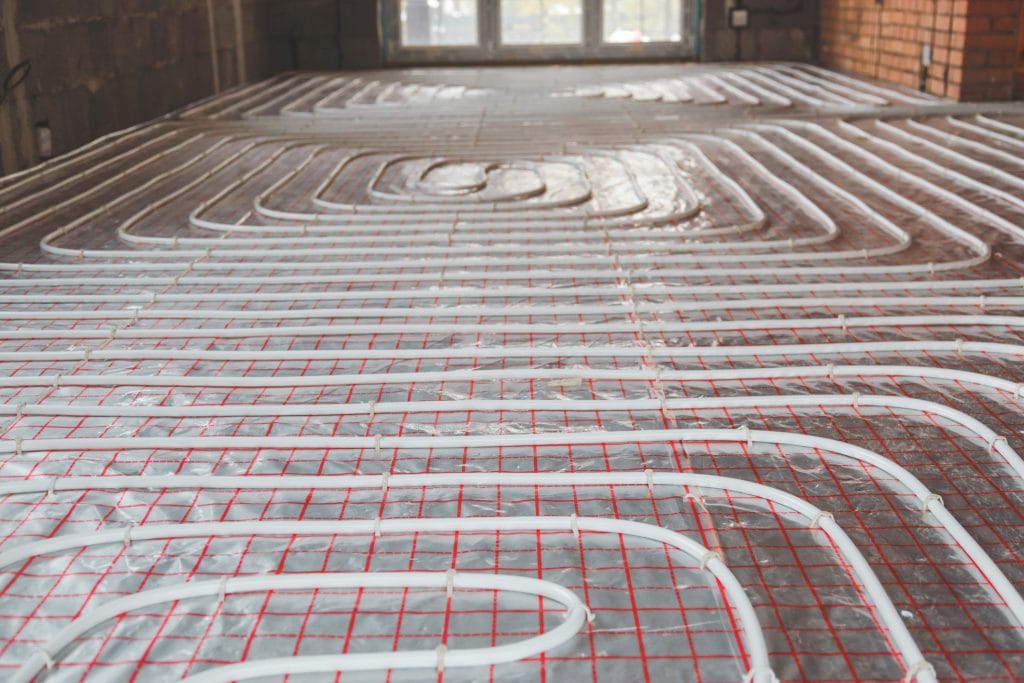
4. Radiant Floor Heating (Hydronic or Electric)

Advantages:
• Provides even heat distribution throughout the home.
• Creates a comfortable indoor environment with no temperature fluctuations.
• Works well in combination with heat pumps.
• Completely silent.
Disadvantages:
• High installation costs, especially for hydronic systems.
• Repairs can be complex and costly.
• Slow to heat, making it unsuitable for quick temperature adjustments.
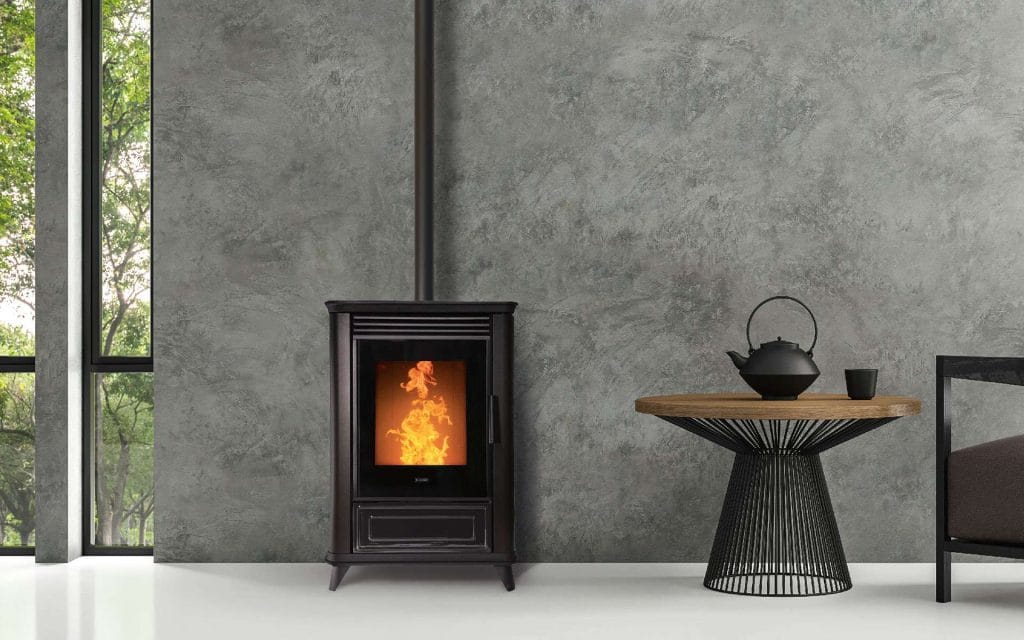
5. Wood or Pellet Stoves

Advantages:
• Great for off-grid homes or areas with limited access to gas or electricity.
• Uses renewable fuel sources (wood or pellets).
• Adds aesthetic value and creates a cozy atmosphere.
Disadvantages:
• Requires regular refueling and maintenance.
• May not provide consistent heating throughout the entire house.
• Needs a dedicated chimney or venting system.
• Fuel costs and availability may vary by location.
Recommendations:
• For mild climates, air-source heat pumps are an efficient and eco-friendly option.
• In colder regions, gas furnaces or a combination of heat pumps and furnaces work well.
• Homeowners in areas with high electricity costs might consider wood or pellet stoves for supplemental heating.
• For new constructions or renovations, radiant floor heating is an excellent long-term investment for comfort.
The choice of a heating system ultimately depends on the local climate, budget, and energy resources available in your region.