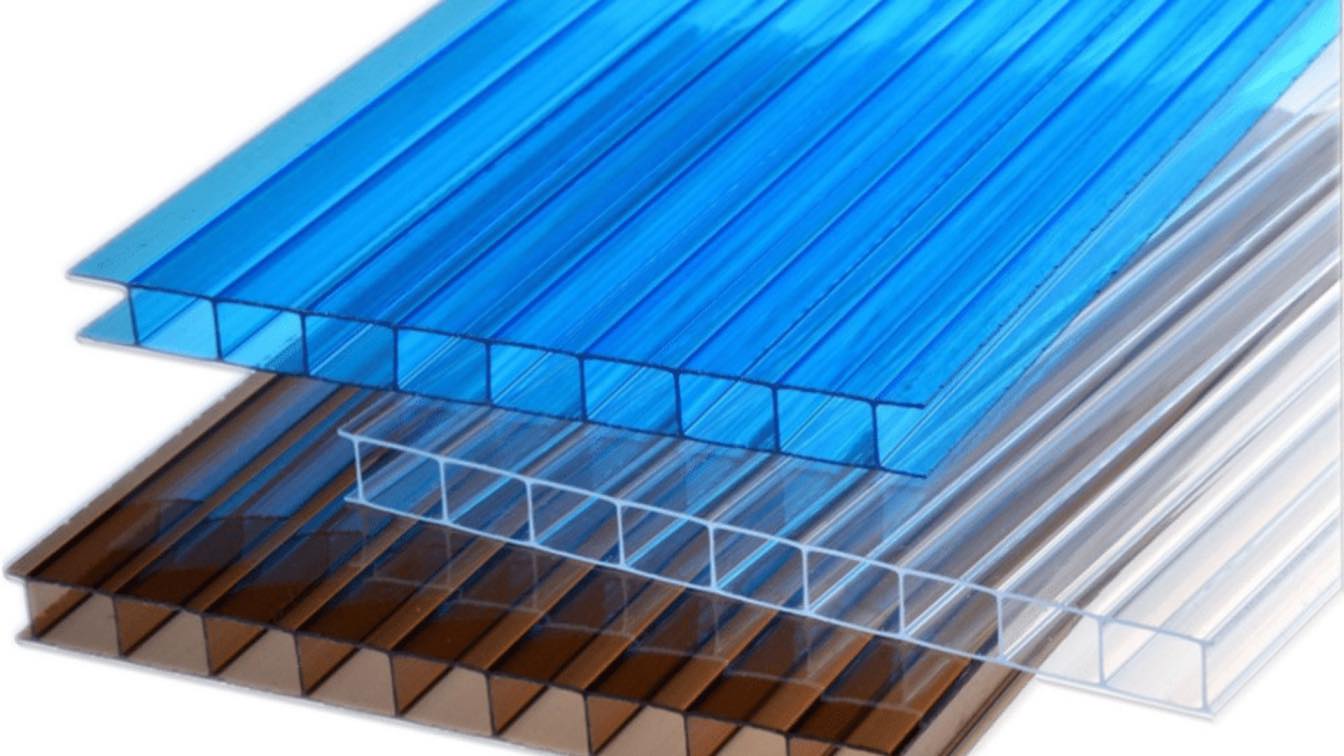
What is Polycarbonate?
Polycarbonate is a lightweight, durable, and versatile thermoplastic material known for its exceptional strength, transparency, and weather resistance. It is produced by polymerizing carbonate groups, resulting in a highly durable material that can withstand impact and environmental stresses.
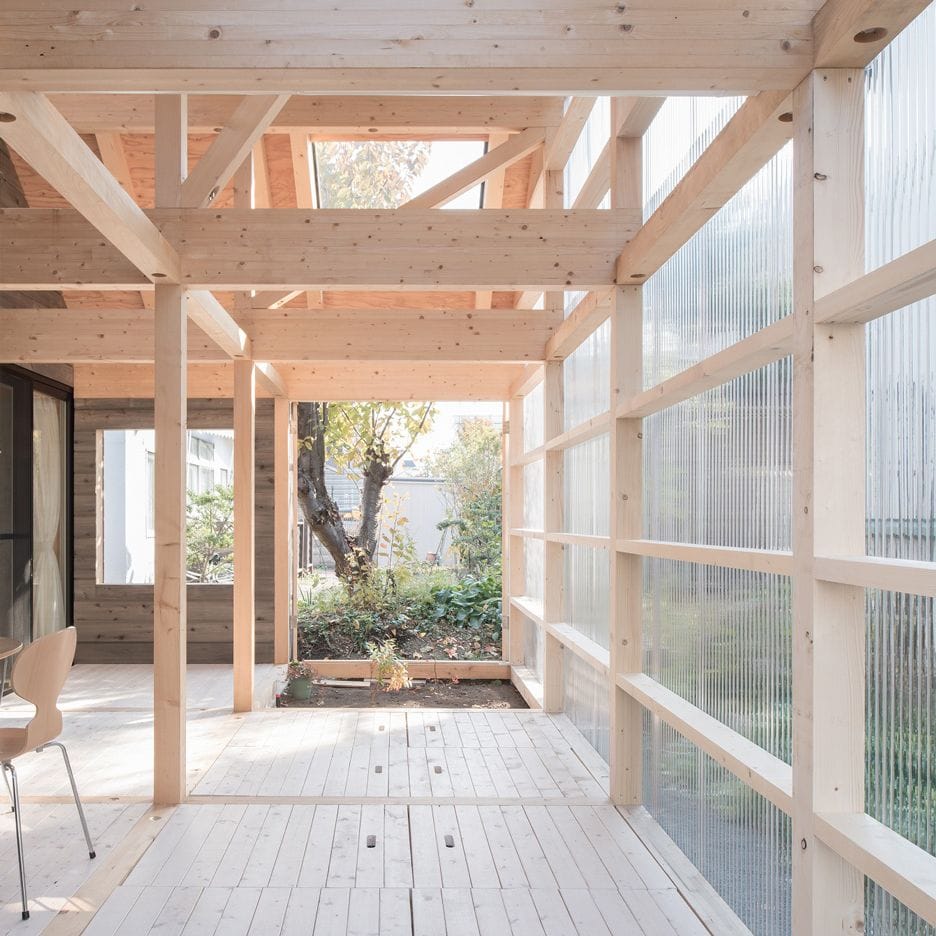
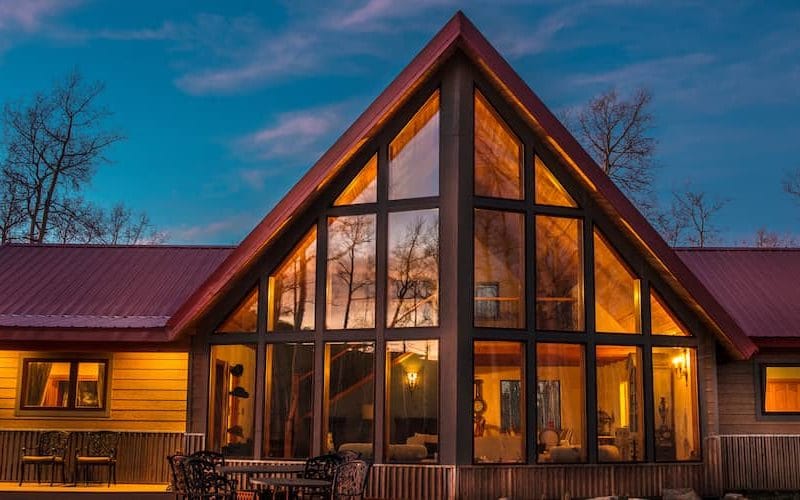
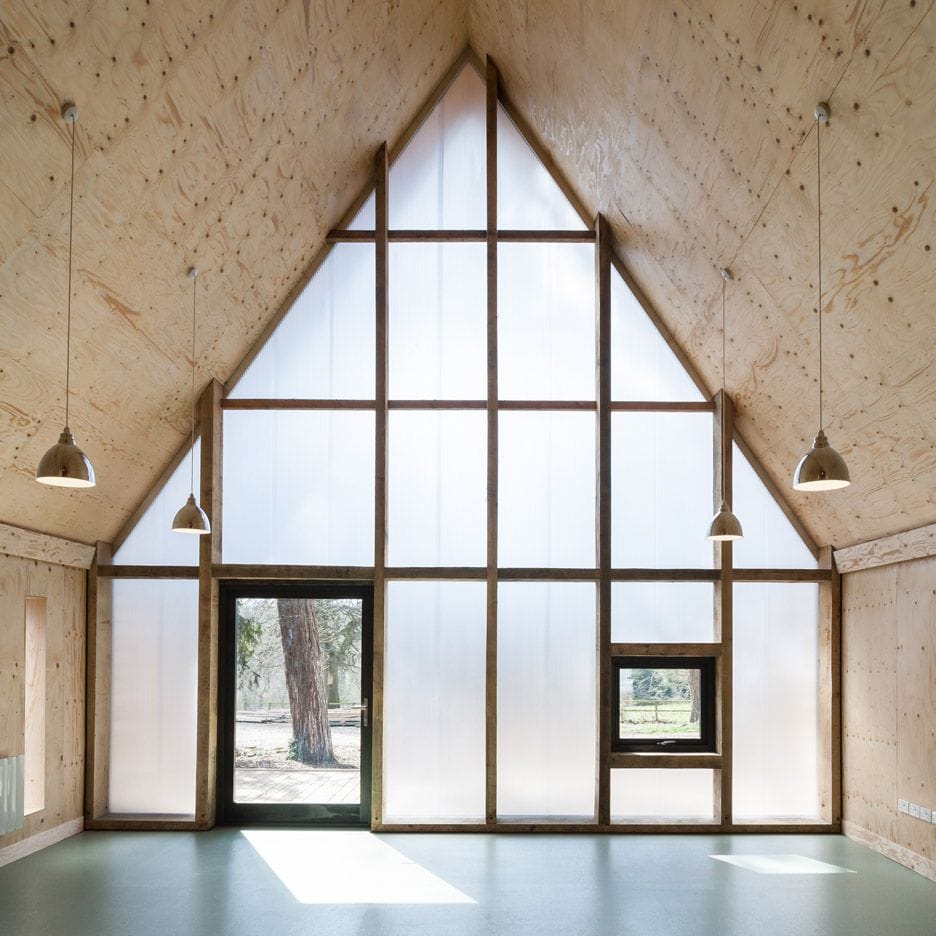
In construction, polycarbonate is widely used for roofing, windows, partitions, and decorative elements. Its unique combination of light weight, strength, and design flexibility makes it a popular choice for modern frame house construction.

History and Origin of Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate was first discovered in 1898 by Alfred Einhorn, but its industrial production began much later. In 1953, Bayer in Germany and General Electric in the United States independently developed methods to produce polycarbonate on a commercial scale. By the 1960s, it was widely used in various industries, including construction.
Today, advances in manufacturing have led to the creation of polycarbonate sheets with improved UV resistance, insulation properties, and structural integrity, making them ideal for residential and commercial applications.
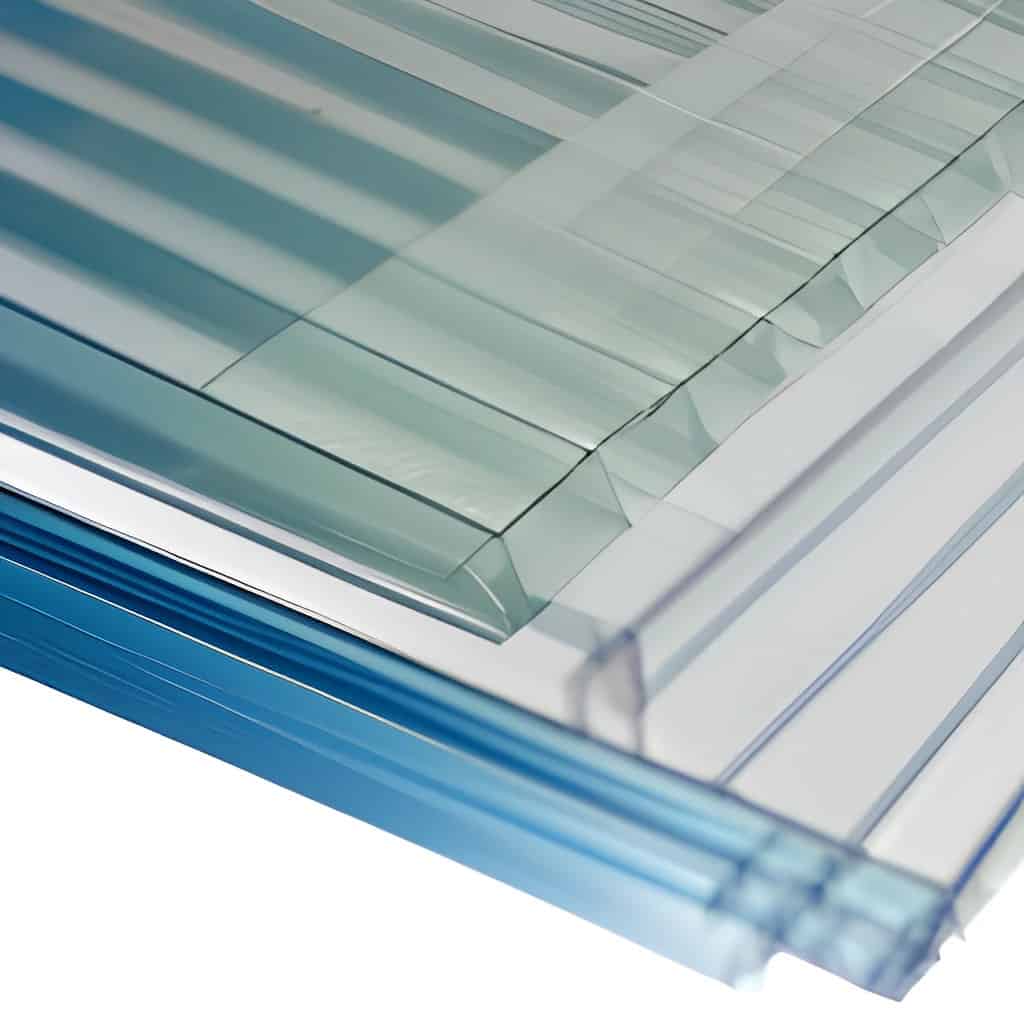
Applications in Frame House Construction
Polycarbonate has become an essential material in frame house construction due to its versatility and performance. Common applications include:
• Roofing: Polycarbonate sheets are often used for translucent or fully transparent roofs, allowing natural light into spaces such as patios, greenhouses, or sunrooms.
• Windows and Skylights: Lightweight and shatter-resistant, polycarbonate is a safer alternative to glass in windows and skylights.
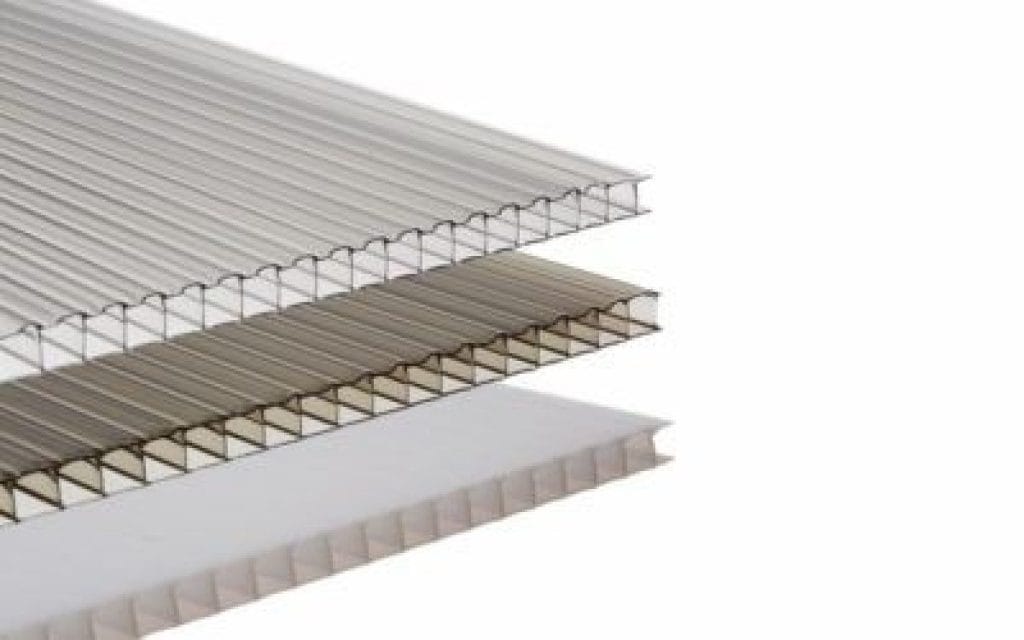
• Partitions and Walls: Double- and multi-wall polycarbonate panels provide excellent thermal insulation, making them suitable for interior partitions or exterior walls in energy-efficient homes.
• Canopies and Awnings: Polycarbonate’s weather resistance makes it ideal for protective structures like carports, entrance canopies, and awnings.
• Decorative Elements: Polycarbonate’s flexibility and availability in a variety of colors allow for unique architectural and design features.
Leading Manufacturers of Polycarbonate
Several companies dominate the global polycarbonate market, offering high-quality sheets and panels for construction applications. Notable manufacturers include:
1. SABIC (Saudi Arabia): Known for producing Lexan™ polycarbonate sheets, a leading product in the industry.
2. Covestro (Germany): A pioneer in advanced polycarbonate technology with a focus on sustainability and innovation.
3. Palram Industries (Israel): Offers a wide range of polycarbonate sheets for roofing, cladding, and decorative applications.
4. Brett Martin (UK): Produces high-performance polycarbonate sheets with UV protection and excellent durability.
5. Plazit-Polygal (Israel): Specializes in multi-wall polycarbonate panels for construction and industrial use.
These manufacturers ensure consistent quality, durability, and innovative solutions to meet the needs of modern construction.

Costs and Economic Feasibility
The cost of polycarbonate depends on the type, thickness, and manufacturer. In the U.S., average prices are as follows:
• Solid Polycarbonate Sheets: $3.00–$5.00 per square foot.
• Multi-Wall Polycarbonate Panels: $1.50–$3.50 per square foot.
• Corrugated Polycarbonate Sheets: $1.00–$2.50 per square foot.
While polycarbonate may be more expensive than some traditional materials like acrylic or glass, its durability, lightweight nature, and low maintenance requirements often make it a cost-effective solution in the long term.
Advantages of Polycarbonate
1. Impact Resistance: Polycarbonate is virtually unbreakable, with a strength that is 200 times greater than glass, making it ideal for high-impact areas.
2. Lightweight: It is significantly lighter than glass or metal, reducing transportation and installation costs.
3. Transparency: Polycarbonate allows up to 90% of light to pass through, making it an excellent choice for skylights and other applications requiring natural light.
4. Weather Resistance: With UV protection and resistance to temperature extremes, polycarbonate performs well in various climates.
5. Thermal Insulation: Multi-wall polycarbonate panels provide superior thermal insulation, enhancing energy efficiency in frame houses.
6. Flexibility: Polycarbonate sheets can be easily bent or molded, allowing for creative architectural designs.
7. Fire Resistance: Polycarbonate has a high fire resistance rating and does not release toxic gases when burned.
Disadvantages of Polycarbonate
1. Cost: High-quality polycarbonate is more expensive than some alternative materials, such as acrylic.
2. Scratch Sensitivity: Polycarbonate can scratch easily, requiring a protective coating for certain applications.
3. Expansion and Contraction: The material expands and contracts with temperature changes, which must be accounted for during installation.
4. Yellowing Over Time: Without proper UV protection, polycarbonate may yellow after prolonged exposure to sunlight.
5. Limited Noise Reduction: Polycarbonate is less effective at blocking noise compared to thicker materials like glass or solid walls.
Conclusion
Polycarbonate is a highly versatile and durable material that has become indispensable in modern frame house construction. Its impact resistance, light weight, transparency, and thermal insulation make it ideal for roofing, windows, partitions, and decorative elements.
While it may have some drawbacks, such as cost and scratch sensitivity, proper installation and the use of high-quality products can mitigate these issues. With innovations in manufacturing and the growing focus on sustainable construction, polycarbonate remains a practical and forward-thinking solution for residential and commercial building projects.